Reactance is divided into inductive reactance and capacitive reactance. The more scientific classification is that inductors (inductors) and capacitive reactants (capacitors) are collectively called reactors. However, since inductors were first created in the past and were called reactors, what people call capacitors now is capacitive reactance, and reactors refer specifically to inductors.
1. Capacitance effect on light no-load or light load lines to reduce power frequency transient over-voltage.
2. Improve the voltage distribution on long transmission lines.
3. The reactive power in the line under light load is balanced locally as much as possible to prevent the unreasonable flow of reactive power and reduce the power loss on the line.
4. When large units are paralleled with the system, the power frequency steady-state voltage on the high-voltage bus is reduced to facilitate synchronous paralleling of generators;
5. Prevent possible self-excited magnetic resonance of generator with long line.
6. When the reactor neutral point is grounded through the small reactor, the small reactor can also be used to compensate the line phase to phase and phase to ground capacitance, so as to accelerate the automatic extinction of secondary arc current, which is convenient for use.
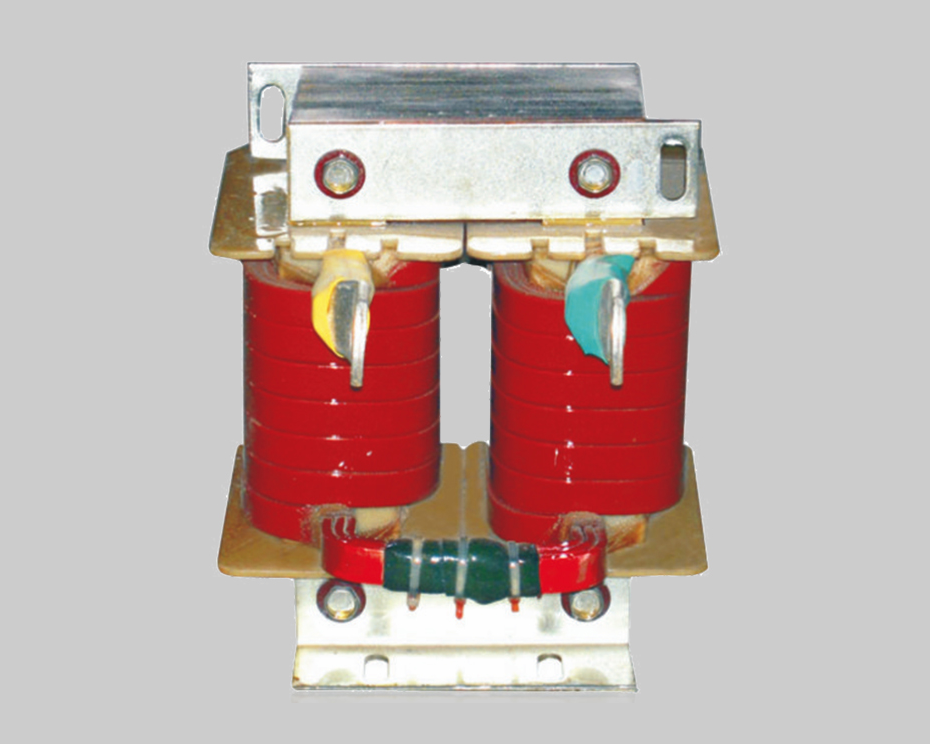
The DC flat wave reactor is mainly used to improve the quality of the power grid and improve the power factor in the circuit.It mainly consists of two parts, the iron core and the coil, iron core is two core pillar structure, core column is made up of silicon steel and the insulating plate, after assembly, screw is pressing down and reduce noise.
3.1 rated operational voltage: 400V-1200V/50Hz
3.2 rated operational current: 3A to 1500A/40C
3.3 electrical strength: iron core -coil 3000VAC/50Hz/10mA/10s without arcing breakdown
3.4 insulation resistance: iron core -coil 3000VDC, insulation value larger than 100M
3.5 reactor noise lower than 65dB (Measuring in distance of 1 meters with reactor)
3.6 protective level: IP00
3.7 insulation level: F level
3.8 production standard: IEC289:1987 reactor
| Model No. | Applicable power (kW) | Rated current (A) | Inductance (MH) | Insulation level | Shape (mm) | Install (mm) | Bore |
| DCL-6 | 0.75 (1.5) | 6 | 10.6 | F, H | 100 × 95 × 115 | 85 × 75 | 5 |
| DCL-10 | 2.2 | 10 | 6.37 | F, H | 100 × 95 × 115 | 85 × 75 | 5 |
| DCL-10 | 3.7 (4.0) | 10 | 6.37 | F, H | 100 × 95 × 115 | 85 × 75 | 5 |
| DCL-15 | 5.5 | 15 | 4.25 | F, H | 100 × 95 × 115 | 85 × 75 | 5 |
| DCL-20 | 7.5 | 20 | 3.18 | F, H | 140 × 140 × 170 | 65 × 70 | 6 |
| DCL-30 | 11 | 30 | 2.12 | F, H | 140 × 140 × 170 | 65 × 70 | 6 |
| DCL-40 | 15 | 40 | 1.6 | F, H | 140 × 140 × 170 | 65 × 70 | 6 |
| DCL-50 | 18.5 | 50 | 1.27 | F, H | 140 × 140 × 170 | 65 × 70 | 6 |
| DCL-60 | 22 | 60 | 1.06 | F, H | 140 × 140 × 170 | 65 × 70 | 6 |
| DCL-80 | 30 | 80 | 0.79 | F, H | 140 × 160 × 170 | 65 × 85 | 8 |
| DCL-110 | 37 | 110 | 0.56 | F, H | 140 × 160 × 170 | 65 × 85 | 8 |
| DCL-120 | 45 | 120 | 0.53 | F, H | 140 × 160 × 170 | 65 × 85 | 8 |
| DCL-150 | 55 | 150 | 0.42 | F, H | 180 × 190 × 210 | 70 × 110 | 8 |
| DCL-200 | 75 | 200 | 0.32 | F, H | 180 × 190 × 210 | 70 × 110 | 8 |
| DCL-250 | 93 | 250 | 0.25 | F, H | 180 × 185 × 260 | 70 × 110 | 8 |
| DCL-280 | 110 | 280 | 0.22 | F, H | 180 × 185 × 260 | 70 × 110 | 10 |
| DCL-300 | 132 | 300 | 0.21 | F, H | 180 × 185 × 260 | 70 × 110 | 10 |
| DCL-400 | 160 | 400 | 0.16 | F, H | 200 × 200 × 230 | 70 × 120 | 10 |
| DCL-450 | 187 | 450 | 0.14 | F, H | 220 × 200 × 290 | 90 × 125 | 10 |
| DCL-500 | 200 (220) | 500 | 0.127 | F, H | 220 × 200 × 290 | 90 × 125 | 10 |
| DCL-600 | 250 (280) | 600 | 0.11 | F, H | 230 × 230 × 290 | 90 × 130 | 10 |
| DCL-800 | 315 | 800 | 0.08 | F, H | 230 × 250 × 290 | 90 × 130 | 10 |
| DCL-1000 | 400 | 1000 | 0.063 | F, H | 240 × 270 × 350 | 155 × 130 | 10 |



